Archives
February 2024
Categories
All
|
Back to Blog
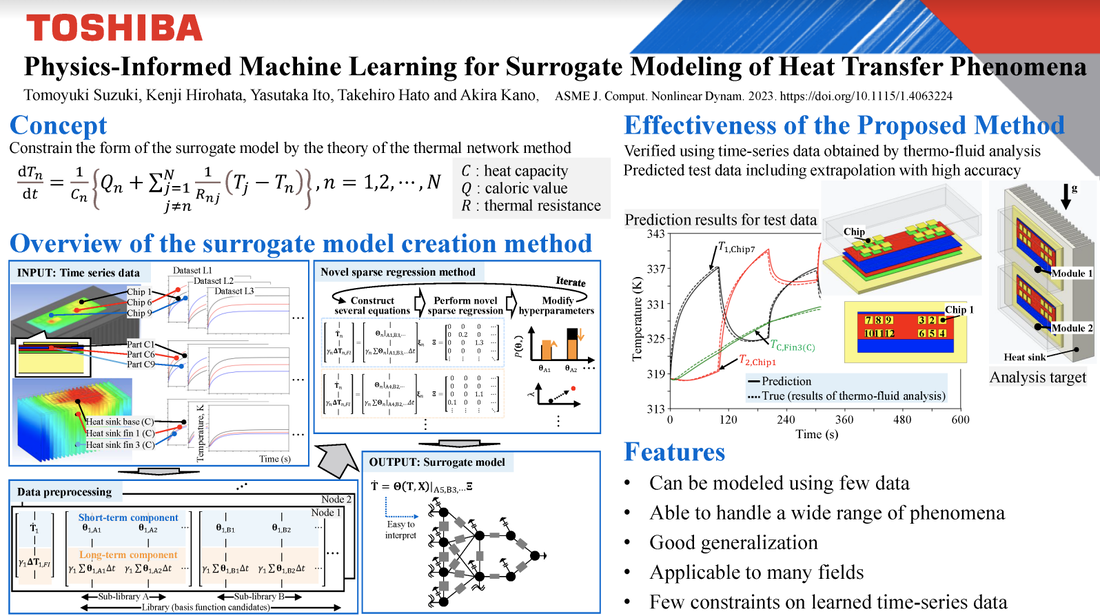
Tomoyuki Suzuki, Kenji Hirohata, Yasutaka Ito, Takehiro Hato, Akira Kano J. Comput. Nonlinear Dynam. November 2023, 18(11): 111001. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4063224 This paper proposes a sparse modeling method for automatically creating a surrogate model for nonlinear time-variant systems from a small number of time-series data. The proposed method is an improvement over a method for sparse identification of nonlinear dynamical systems first proposed in 2016, for application to temperature prediction simulations. The form of the thermal model is constrained by the physical model, and we use three novel machine-learning methods to efficiently estimate the model parameters. We verify the proposed method’s effectiveness using time-series data obtained by thermo-fluid analysis of a power module mounted on a comb-shaped heat sink. The proposed method has potential applications in a wide range of fields where the concept of equivalent circuits is applicable. Because the proposed method requires few data, has high extrapolation accuracy, and is easily interpreted, we expect that design parameters can be fine-tuned and actual loads considered, and that condition-based maintenance can be realized through real-time simulations.
0 Comments
Read More
Back to Blog
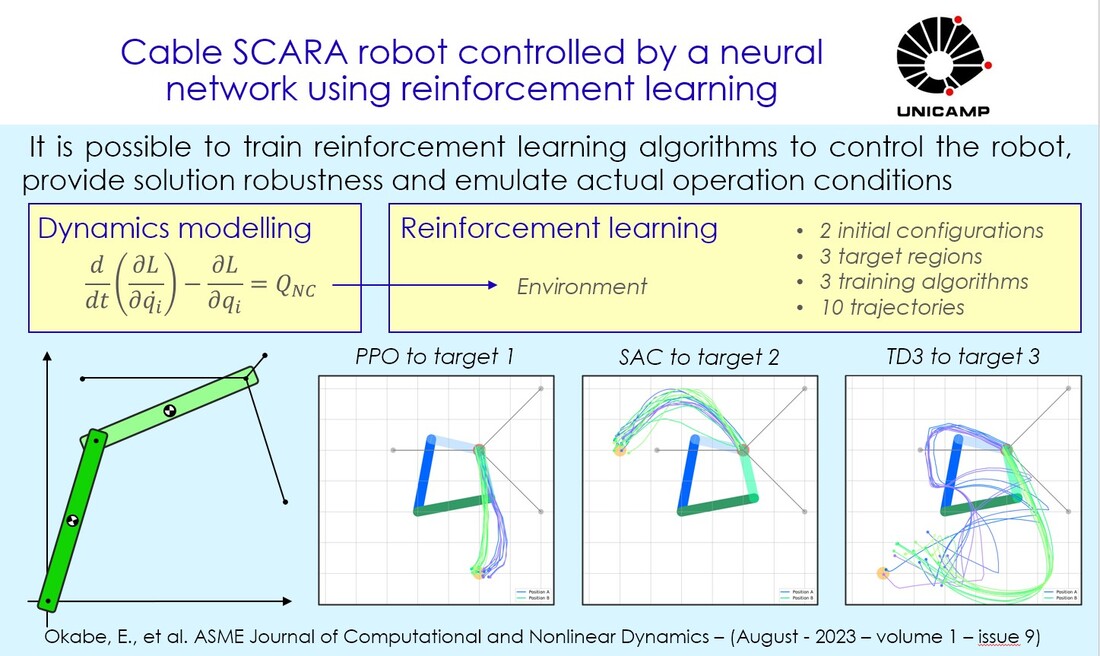
Eduardo Okabe, Victor Paiva, Luis Silva-Teixeira, Jaime Izuka J. Comput. Nonlinear Dynam. Oct 2023, 18(10): 104501 https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4063222 The industry and the scientific community have shown interest in SCARA (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm) robots due to their high accuracy. In this paper, a two-link SCARA has its end-effector pulled by three cables that generate a triangular-shaped workspace. Moving the end-effector in this region is a relatively straightforward task, but placing the end-effector outside it requires a nonlinear dynamic model and a state-of-the-art controller. To address this problem in a simpler, more efficient and innovative manner, the equations of motion are derived and three reinforcement learning algorithms are employed: Proximal Policy Optimization (the same used by the chatbot ChatGPT), Soft Actor-Critic and Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient. Three targets outside the triangular workspace are considered and the trained networks have their results compared in terms of displacement error, velocity and standard deviation. The Twin Delayed Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient provides creative trajectories, the Soft Actor-Critic presents better solutions for two out of three targets, while the Proximal Policy Algorithm appears to be the most consistent considering all targets under analysis.
|
 RSS Feed
RSS Feed